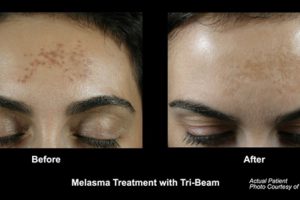
Melasma is a skin discoloration condition that causes darkened, brown patches of skin to develop across the face. It is occasionally misdiagnosed as hyperpigmentation – however, the causes and treatments for melasma are vastly different. It is important to seek professional advice to be sure you are not misdiagnosed.
Who can get melasma?
It’s a common condition that affects people of all ages, from young children and teens to adults and the elderly – it is much more common with women that have darker skin. It can be precipitated by pregnancy nicknamed ‘the mask of pregnancy’, or after using birth control pills. Around 10%-15% of women experience a level of melasma during pregnancy.
How do you know it’s melasma?
If you are male, it is less likely that you are suffering from melasma – as it is a predominantly female condition. Melasma is characterized as dark brown blotches of skin, usually around the forehead, cheeks, nose and lips. The patches will usually darken over a long period of time, often several months, and are equally distributed on both sides of the face. If you are ever unsure about the nature of skin changes, it’s best to seek out the advice of a medical practitioner.
What causes melasma?
At present, there isn’t a predominantly accepted cause for melasma. Many factors including hormone, medications, sun exposure, heat, and environment can contribute to the condition. Hormonal fluctuations, along with UV exposure and a genetic predisposition to skin conditions are also considered to be possible causes.
Statistically, melasma tends to affect people with darker skin tones more often – particularly women of South East Asian, Hispanic or Central Asian descent.
What are the treatments?
The first step in treating melasma is proper skin care. Patients are prescribed daily sunscreen with iron-oxide, or topical medications such as hydroquinone, retinoic acid, kojic acid, and azelaic acid. These can often lift the darkness of the blotches, or completely eradicate mild cases.
There are also cosmetic procedures that have been shown to have been incredibly efficacious on treating melasma:
Oral Medications:
Oral tranexamic acid is a novel treatment used to treat melasma. It is a safe therapeutic option which is easy to administer with few mild side effects. The medication was originally approved for patients with blood clotting disorders, however studies have shown that tranexamic acid does not increase the risk of thromboembolism. It is important for the doctor prescribing the medication to carefully screen each patient for risks prior to initiating therapy. Results are normally seen after 8-12 weeks of treatment.
Peels done in conjunction with a microdermabrasion are used to remove the top layer of the skin and reveal youthful skin beneath. The dead skin is sloughed away, taking irregular pigmentation and texture with it. There are several different types of peel, including: alpha hydroxy acid, beta hydroxy acid, and trichloroacetic acid that are used for melasma.
Fractionated laser skin treatments are very effective and have minimal downtime. Patients will usually need 5-8 treatments once every 3-4 weeks in order to reduce the pigmentation in the skin. Results build up over a course of treatments, meaning that you are in control of the results.
There are now many treatments available for effective treatment of melasma and women are not expected to carry it with them for life. Post-pregnancy, Dr Melamed can advise on the depth of procedure required, after care and predicted results.
Schedule an online appointment, or give us a call.